
As homeowners, when there is a major capital expenditure, like a new roof, we call a few contractors to get some competitive bids. Then, we ask a few questions, maybe check some references, and hire the contractor with the lowest cost that we feel will meet our needs.
As board members or managers of community associations, however, the jobs are larger and the money involved is far greater. This also means that the risks and potential liability are increased as well.
For example, the simple task of obtaining competitive bids can result in quotes that are widely divergent. Because costs are greater, the variation can be significant. Criterium Engineers has often been called by property managers to help explain why contractor bids are so far apart. The answer most often is that the quotes are not truly comparable. In other words, it’s not apples to apples. In order to compare bids, we require detailed construction specifications, without them a project is likely going to fall off track and budget.
Roof replacement is one good example. Different contractors may choose different materials. One may remove the old roof; another may not. One may include costs for permits, disposal, and cleanup; another may not.
The way to get comparable bids is through a specifications process. It is also the way to get a job that meets your needs and perhaps considers money-saving alternatives. A specification prepared by a licensed Professional Engineer is almost certain to include elements that you may never have thought of and ultimately protect your interests as a manager, board member, and as an owner.
What are Construction Specifications?
Construction Specifications are a set of documents that define the scope of the job and the expectations for the contractor. Among other things, it generally includes:
- Drawings that illustrate construction details
- Documentation of:
- All things that must be covered by the quote
- The manner and format in which the quote is to be provided
- Methods and materials to be employed (see below)
- Conditions under which the work is to be performed (e.g., not before 8AM or after 6PM)
- Required insurances
- Form of agreement to be used
- Warranties to be provided
- Responsibilities of the association vs. the contractor
- Procedures for effecting changes
- Construction schedule
- Terms of payment
- Site conditions that must be maintained before, during, and after the work is complete
- Standards and regulations that may govern the work
There are two types of construction specifications, generally referred to as Performance Specs and Prescriptive Specs. In a Performance Specification, the engineer lays out the expectations for the job, that is, how the systems and materials are to perform now and over time, leaving it to the contractor to identify those systems, materials, and method of installation to accomplish the objectives of the specification. For example, a Performance Specification for a roof could be as theoretical as that it must keep the rain out under all conditions and must last 20 years. In more practical terms, the specification may state the type of roof (e.g., EPDM) but decline to name the manufacturer, method of adherence, etc.
A Prescriptive Specification, as the name implies, lays out much more specifically how the job is to be done, what materials are to be used, and the manner in which they are to be installed. For example, a Prescriptive Specification for a roof would most likely list the type AND manufacturer, all details and methods of fastening, etc.
Engineers generally rely on a variety of standard specifications from entities such as the Construction Specifications Institute (CSI) and MasterSpec (AIA). These documents serve as a framework, providing boilerplate and standard clauses, but a true and good specification starts with a field visit to observe actual conditions, and then continues with research to select the right approach.
Value Engineering and Construction Specifications
Developing a specification is the perfect time to consider alternative approaches for the repair or replacement of key systems. Sometimes, a new approach can result in cost savings over the original design. At other times, a different approach may result in greater durability or reliability, thereby reducing costs over time, even though the initial outlay may be more expensive now. Value is the relationship between cost and benefit. Value Engineering, when properly done, is more specifically about the relationship between cost and function. It is generally a “like for like” substitution that generates a cost savings, either initially or operationally, without sacrificing function, intent, or performance of the original design. When developing a specification, the engineer can either perform the Value Engineering himself (Prescriptive Specification) or ask the contractor to propose alternatives (Performance Specification). Either way, the association wins.
Liability for the Board and Property Manager
One of the key differences between owning your own home and sitting on a board representing a group of owners is that you now have a fiduciary responsibility to those owners.
While most board members would not think of awarding a contract to someone just because he was a friend, it can be just as risky to hire any contractor if proper care in the selection has not been exercised. The engineer that developed the specification is also able to assist with pre-bid meetings, contractor selection, and kick-off meetings.
To illustrate how serious this can become, we were recently subpoenaed to produce documents in a case that involved shoddy work by a contractor. While the contractor is the key defendant, so are previous board members and the property manager. Being able to demonstrate that contractor selection followed an industry-accepted, professional, and objective procedure is your best defense in such a case.
Conclusion
Developing a specification for any significant capital expenditure is the best way to ensure comparability of contractor bids, a quality job, and avoid exposure to liability. The best part is, it may actually save money on the overall job. Specifications are developed by engineers or architects who are familiar with the design and installation of building systems. If chosen properly, that person could well be the same engineer who originally developed your reserve study and is familiar with your specific property. We would also strongly recommend hiring that same engineer to monitor the actual construction, repair, or replacement to ensure compliance with the specification. That’s why a local, experienced engineer is the best choice “For the Life of Your Association.”
Learn more about our Construction Management and Monitoring services.

 Make sure you actually need one, too
Make sure you actually need one, too
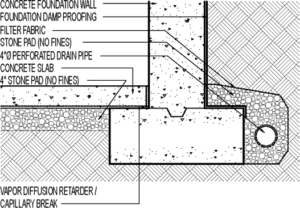
 fing the outside of the foundation walls and/or
fing the outside of the foundation walls and/or