Moisture: The Root of all Maintenance

One of the primary issues in building science is the study of how moisture damages buildings and reduces the quality of life of its inhabitants. Moisture penetration can cause mold, rot, and interior damage. Serious moisture problems and their cure are often hard to solve as the physics of air flow, dew points, and vapor transmission can be complicated even with invasive inspections and the introduction of modern tools such as infrared scanning and moisture meters. As these more difficult problems will need a longer article to fully explore, let us focus instead on the more common problems faced by homeowner association and condo boards.
Leaking Foundations
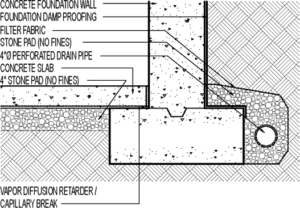
Foundations are usually constructed with poured concrete or concrete block. Modern foundations are protected with a waterproof coating on the exterior surface and a foundation drain around the foundation perimeter at the base of the footing, often with an under-slab drainage system with an associated sump pump. With these operating properly, basements should be dry. If a modern foundation (less than 30 years old) experiences water infiltration, something is not working right and the source is probably surface water. If someone tells you it is due to rising ground water, be skeptical. Keep in mind the water table is the depth in the earth that is permanently saturated with water. According to the building code, modern foundation basement slabs are built above the water table. If the water table is too high, then the building will not have a basement but rather it will be built on a slab on grade. If you have any question about where the water table is, the municipal code officer or a local foundation excavating contractor can help.
Two-Step Approach
If your foundation is leaking, you need a two-step action plan. First, fix the wall problem allowing water to infiltrate into the basement and second, minimize surface water reaching the exterior of your foundation wall. As it will prove difficult and expensive to re-apply waterproofing to the exterior wall, the typical repair is a pressure injection of polyurethane or other type of foam product into cracks in the wall. The second step is just as important.
Surface water comes from a variety of sources. It can be rain or snow melting on the roof, rain falling on the soil near the foundation, or water from nearby sloping land. Roof gutters are supposed to divert water away from the building, but often they are the primary source of water to the ground around the foundation. Gutters are often poorly designed – either they are undersized in handling the flow of water off the roof area, do not have enough downspouts to handle the quantity of run-off water, or the gutter/downspout is broken or incorrectly placed.
If gutters are installed too low at the roof edge, steep roofs will create a velocity in the laminar flow of water to overshoot the gutter during heavy rain events. Downspouts often discharge their water near the foundation rather than diverting it away from the wall. I recommend adding a minimum six-feet extension to the end of the downspout. Furthermore, you should treat the drip edge area along the foundation wall as a ‘secondary’ roof. By this I mean, you should seal the drip edge from allowing water from the roof or other source to enter the soil near the foundation.
Keep in mind the soil has been cultivated and it absorbs water readily. Newer homes also have the problem of the soil along the foundation being backfill soil that is not compacted well, allowing easy water passage, in effect creating a short circuit from the roof to your basement. This soft soil also is susceptible to settlement, creating a place for water to pool or cause erosion allowing even more water to enter the soil.
To prevent this problem, you must first create a positive slope on the surface away from the foundation. A good rule of thumb is to create a slope dropping three inches over six feet. Once the proper slope is in place, cover it with 6 mil poly plastic approximately 18 inches wide along the foundation perimeter. This is your “secondary’ roof preventing water from entering the soil. Cover this waterproof barrier with stone or other suitable material to prevent the poly sheet from moving.
You may also have to slope the land nearby to prevent your neighbor’s land from contributing to your surface water. This can be done with shallow surface ditches called swales or buried ditches called French drains. This type of drain is a trench at the foot of a slope shedding water toward your home designed to intercept surface water from reaching your foundation wall. Buried in the trench is a perforated pipe to divert water. Your landscaper or property manager can provide details on available options. With a logical plan, you can have the dry basement you deserve.


 fing the outside of the foundation walls and/or
fing the outside of the foundation walls and/or